 |
| August 23, 2016 | Volume 12 Issue 32 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Choosing a stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 Lin Engineering stepper motors are widely used in various applications that require precise control of motion, such as in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical equipment. There are two main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. Learn the differences, advantages, and when to use one type or the other.
Lin Engineering stepper motors are widely used in various applications that require precise control of motion, such as in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical equipment. There are two main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. Learn the differences, advantages, and when to use one type or the other.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
Top Product: Integrated servo system is 20% smaller than standalone unit
 Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive unit is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive unit is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Read the full article.
Overhung load adaptors provide load support and contamination protection
 Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Learn more.
Why choose electric for linear actuators?
 Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Get this informative e-book. (No registration required)
New AC hypoid inverter-duty gearmotors
 Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Learn more.
Next-gen warehouse automation: Siemens, Universal Robots, and Zivid partner up
 Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Read the full article.
Innovative DuoDrive gear and motor unit is UL/CSA certified
 The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
Learn more.
BLDC flat motor with high output torque and speed reduction
 Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Learn more and view all the specs.
Application story: Complete gearbox and coupling assembly for actuator system
 Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Read this informative GAM blog.
Next-gen motor for pump and fan applications
 The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
Learn more.
Telescoping linear actuators for space-constrained applications
 Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Learn more.
Competitively priced long-stroke parallel gripper
 The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
Learn more.
Extend your range of motion: Controllers for mini motors
 FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
Learn more.
When is a frameless brushless DC motor the right choice?
 Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
View the video.
Tiny and smart: Step motor with closed-loop control
 Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Learn more.
Chock full of exciting technology firsts, NASA's Asteroid Redirect Mission completes robotic design milestone
From moving asteroids to electric space propulsion to bringing space boulders to the moon, this project is chock full of technological daring.
NASA is developing a first-ever robotic mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid, collect a multi-ton boulder from its surface, and redirect it into a stable orbit around the moon. Once it's there, astronauts will explore it and return with samples in the 2020s. This ambitious, multi-stage project is part of NASA's plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.

In the Robotics Operation Center at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, an engineering development unit of the robotic capture system is tested at full scale. [Credits: NASA]
Following a key program review, NASA approved the Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) to proceed to the next phase of design and development for the mission's robotic segment. ARM is a two-part mission that will integrate robotic and crewed spacecraft operations in the proving ground of deep space to demonstrate key capabilities needed for NASA's journey to Mars.
The milestone, known as Key Decision Point-B, or KDP-B, was conducted in July and formally approved by agency management Aug. 15. It is one in a series of project lifecycle milestones that every spaceflight mission for the agency passes as it progresses toward launch. At KDP-B, NASA established the content, cost, and schedule commitments for Phase B activities.

Before beginning its trip to lunar orbit, the ARM spacecraft will demonstrate a widely supported asteroid deflection technique called a gravity tractor. The spacecraft plus the mass of the captured boulder will create a small gravitational attraction to alter the orbit of the large asteroid. [Credits: NASA]
The mission's main thrust
The robotic ARM (editor's note: "ARM" is the project acronym, not a literal robotic arm) will demonstrate advanced, high-power, high-throughput solar electric propulsion; advanced autonomous high-speed proximity operations at a low-gravity planetary body; controlled touchdown and liftoff with a multi-ton mass from a low-gravity planetary body, astronaut spacewalk activities for sample selection, extraction, containment, and return; and mission operations of integrated robotic and crewed vehicle stack -- all key components of future in-space operations for human missions to Mars.
The robotic component of the ARM mission will demonstrate the world's most advanced and most efficient solar electric propulsion system as it travels to a near-Earth asteroid (NEA). NEAs are asteroids that are fewer than 121 million miles (1.3 AU) from the sun at the closest point in their orbit. Although the target asteroid is not expected to be officially selected until 2020, NASA is using 2008 EV5 as the reference asteroid while the search continues for potential alternates.
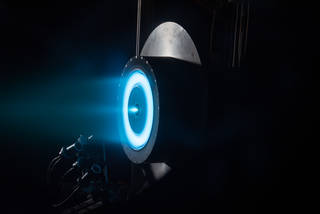
The HERMeS (Hall Effect Rocket with Magnetic Shielding) Technology Development Unit thruster exceeds over 1,300 hours of operational wear testing in a vacuum facility at the NASA Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, OH. Magnetic shielding protects the walls of the thruster from erosion, a major breakthrough in Hall thruster design that could hold the key to long-life, reusable electric propulsion systems. [Credits: NASA]
What makes a target asteroid such as 2008 EV5 particularly appealing to the scientific, exploration, and industrial communities is that it is a primitive, C-type (carbonaceous) asteroid, believed to be rich in volatiles, water, and organic compounds. The ability to extract core samples from the captured boulder will allow scientists to evaluate how its composition varies with depth and could unlock clues to the origins of our solar system. Astronaut sampling and potential commercial activities could indicate the value of C-type asteroids for commercial mining purposes, which in turn could have significant impacts on how deep space missions are designed in the future.
After collecting a multi-ton boulder from the asteroid, the robotic spacecraft will slowly redirect the boulder to an orbit around the moon, using the moon's gravity for an assist, where NASA plans to conduct a series of proving ground missions in the 2020s. There, astronauts will be able to select, extract, collect, and return samples from the multi-ton asteroid mass, and conduct other human-robotic and spacecraft operations in the proving ground that will validate concepts for NASA's journey to Mars.

In the Spacecraft Structures Lab at NASA's Langley Research Center, Asteroid Redirect Mission robotic contact and restraint system is prototyped and tested. [Credits: NASA]
Meeting objectives and setting new ones
Earlier this year, NASA updated the target launch date for the robotic mission to December 2021 in order to incorporate acquisition of the industry robotic spacecraft development into the project schedule. To reflect this new target date, the project's cost cap was increased at KDP-B from $1.25 billion to $1.4 billion. This figure does not include the launch vehicle or the post-launch operations phase. The crewed segment, targeted for launch in 2026, remains in an early mission concept phase, or pre-formulation.
During Phase B of the robotic mission, the program will develop a baseline mission design to meet requirements consistent with NASA's direction on risk, cost, and schedule, and will conduct an independent review of the baseline project design.
Completing KDP-B is a catalyst for increased external involvement in the robotic mission development, explained Michele Gates, program director for ARM at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
"Since its early formulation, NASA has invited mission concept feedback and development ideas from the planetary science community, general public, U.S., and global industry, and international partners," said Gates. "With KDP-B under our belt, ARM can now move forward to define partnerships and opportunities for long-term engagement."
The robotic ARM project, led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, CA, will issue a request for proposals for the spacecraft to a set of aerospace companies that previously worked with the ARM robotic design team on a six-month study of spacecraft concepts to meet mission requirements. KDP-B serves as authority for JPL to proceed with the next procurement phase.
NASA plans to issue a solicitation in September that will include a call for partner-provided payloads on the robotic flight system. This call is in addition to potential cooperation under discussion with the Italian Space Agency. NASA will provide spacecraft integration, power, data storage, and communication capabilities for selected payloads, which the agency will choose based on contributions to both partner goals and ARM objectives, with consideration for those that may support risk reduction for the mission.
This solicitation also will include a membership call for an ARM Investigation Team, which will be a multidisciplinary group of U.S. industry, academia, government, and international members. The Investigation Team will operate on an initial three- to five-year term, providing technical expertise to the ARM robotic and crewed project teams.
The team will conduct analyses of spacecraft and mission design, and investigate concepts to support robotic mission objectives, including overall science, planetary defense, asteroid resource use, and deep-space capability demonstrations. Led out of NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA, the Investigation Team work will continue some of the research conducted by the ARM Formulation Assessment and Support Team, which helped define mission concepts and inform mission requirements and risks over a three-month period in 2015.
Source: NASA
Published August 2016
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

